Let's Simply Talk about AFib Treatments

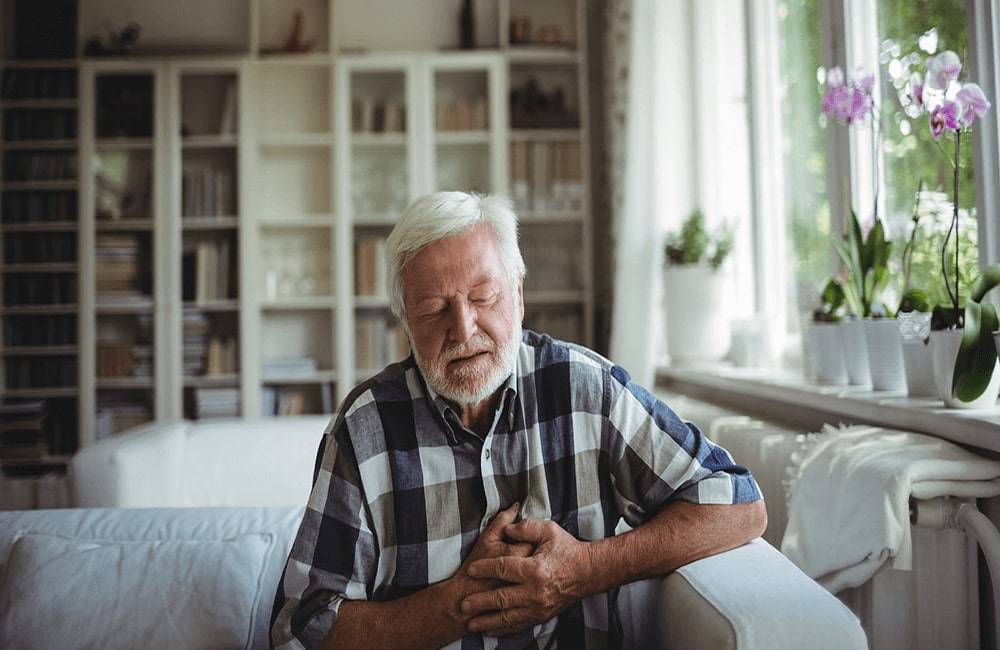
Palpitations, panic, dizziness, shortness of breath ...... Believe that many people have experienced this situation, but you do not know what is happening. Once there is a slight improvement, it will not be a concern of most of them. In fact, we should all be alert to the above symptoms, it may be atrial fibrillation!
AFib is a serious hazard to human health, affecting the quality of life in light cases, and can cause disability and death in serious cases. What are the consequences of atrial fibrillation? And what is the most common treatment for atrial fibrillation? Let's have a simple understanding.
What are the consequences of atrial fibrillation?
As the saying goes, good comes out of working together. When the heartbeat is not in unison, the cardiovascular system naturally does not work well. It affects the body in two main ways.
1. Inadequate Blood Supply
The heart acts as a pump, constantly pumping back the venous blood and then pumping out the arterial blood to maintain the blood supply needed by the body. However, if it pumps very quickly, it can only pump a little bit at a time, so the amount of blood that can be pumped out becomes very small. Patients may experience panic and precordial discomfort, and sometimes even fainting, due to the lack of blood supply.
2. Increased Risk of Thrombi (Blood Clots)
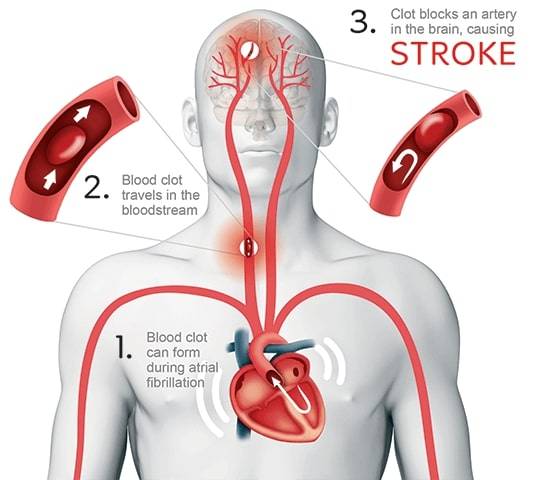
In normal people, the blood flows quietly like a stream, but in patients with atrial fibrillation, it is not so calm. When blood flows through an irregularly fibrillating atrium, it can easily form eddies, which greatly increases the risk of thrombosis. Thrombosis is like sediments of a small stream coalescing into large stones, which will flow to all parts of the body with the blood circulation and block the blood vessels in the corresponding parts.
If the blood clot flows to the blood vessels in the brain, it can lead to brain embolism and cerebral infarction (i.e. ischemic stroke). If the blood clot "runs" to the legs, then it may block the blood vessels in the legs, which can cause ischemic necrosis in serious cases.
TREATMENTS FOR afib
1. Drug Therapy (Pharmacotherapy)

There are no drugs that can eradicate atrial fibrillation. Medications can reduce or alleviate atrial fibrillation episodes and keep some patients free of episodes for a significant period of time, but the focal origin of AFib remains and will continue to be present. Therefore, the main goal of drug therapy is to "stabilize" the state.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: such as propafenone, ibutilide, amiodarone, etc.
- Drugs to maintain sinus rhythm: amiodarone, ibutilide, dronedarone, sotalol, etc.
- Drugs for rhythm control: metoprolol, amiodarone, digoxin, diltiazem, etc.
- Drugs regarding upstream therapy: ACEI, statin, antioxidants, etc.
2. Anticoagulation Therapy

The incidence of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation is 3-5 times higher than in the normal population, whether it's paroxysmal AFib or persistent AFib. Anticoagulation is an effective way to prevent strokes. It is also a consistent treatment throughout the whole treatment of atrial fibrillation. Anticoagulation is initiated according to the patient's CHADS2 score (congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥75 years, diabetes mellitus, stroke).
Anticoagulation must be supervised by a specialist. Excessive anticoagulation may lead to bleeding, while insufficient anticoagulation has no preventive effect.
3. Non-pharmacological Treatments for Atrial Fibrillation
(1) Electrical Cardioversion (Conversion to Sinus Rhythm)
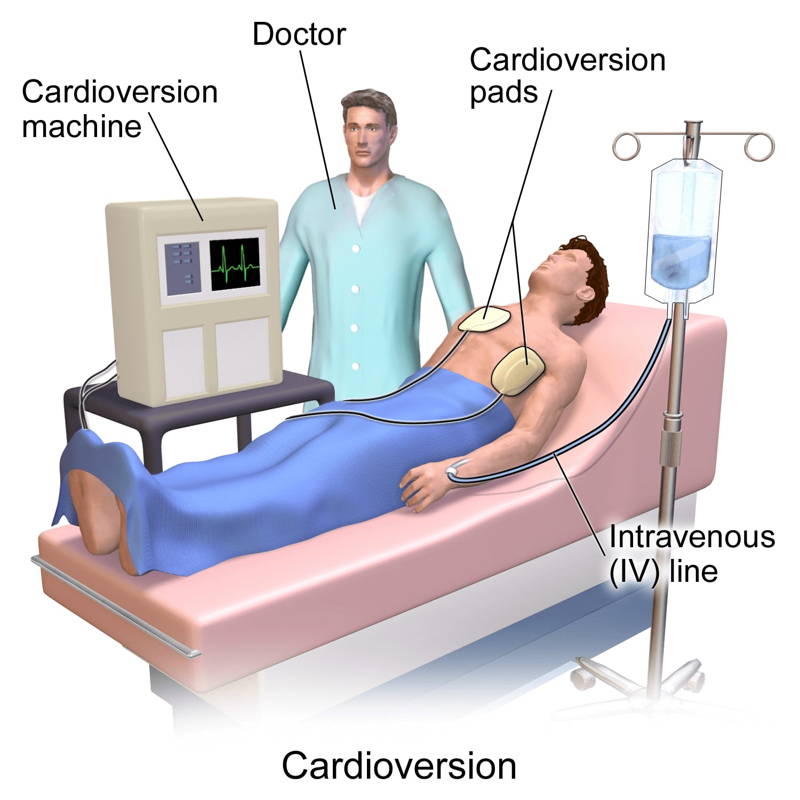
It is a method of restoring sinus rhythm by using two electrode pads placed in the appropriate part of the patient's chest and distributing an electric current through a defibrillator.
Electrical resuscitation is indicated for: emergency atrial fibrillation (such as myocardial infarction, extremely fast heart rate, hypotension, angina pectoris, heart failure, etc.), atrial fibrillation with severe symptoms that are difficult for the patient to tolerate, atrial fibrillation that was successfully resuscitated last time and has recurred without maintenance with medication.
Electrical cardioversion is not a complete cure for atrial fibrillation. The patient's atrial fibrillation often recurs, and some patients need to continue to take antiarrhythmic drugs to maintain sinus rhythm.
(2) Radiofrequency Ablation & Catheter Ablation
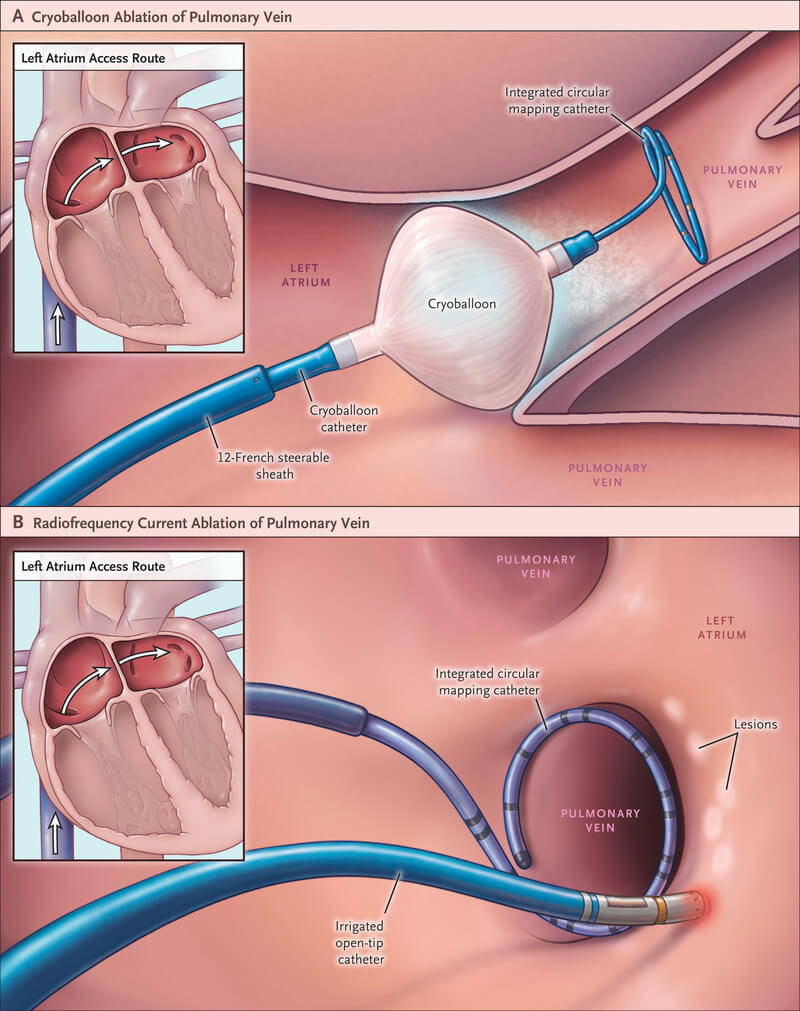
Atrial fibrillation ablation treatment can improve the quality of life. It is suitable for most patients with atrial fibrillation and is less invasive and easily accepted by patients.
Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation is a technique that has gained popularity in the last 20 years and is a method that can eradicate atrial fibrillation lesions and achieve complete treatment.
Radiofrequency ablation is feasible in patients with symptomatic persistent atrial fibrillation with or without pharmacological treatment.
(3) Surgical Maze Surgery
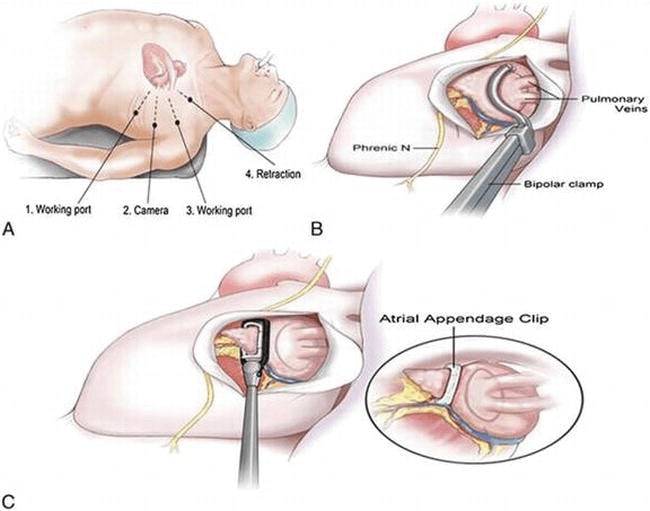
Currently, it is mainly used for patients with atrial fibrillation who need cardiac surgery due to other heart diseases. The surgery is effective for complete eradication of atrial fibrillation but invasive.
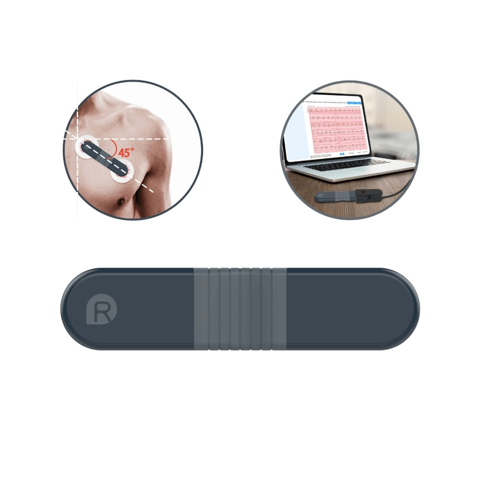
Shall you do radiofrequency ablation or not? Shall you take anticoagulants? All these questions can be safely and boldly thrown to your doctor! All you can do is to pay attention to your ECG report, change your bad habits and actively cooperate with your treatment. By the way, Wellue's 24-hour ECG Recorder with AI Analysis can help you manage your ECG data easier thanks to its highly portability, wireless ambulatory ECG monitoring and effective AI analysis.