Pulse Dose Delivery vs. Continuous Flow
Pulse Dose Delivery vs. Continuous Flow
What is the difference between pulse dose delivery and continuous flow in portable oxygen concentrators?
Both pulse-flow and continuous-flow portable oxygen concentrators (POC) provide supplemental oxygen to users who require it, but they differ in their delivery methods and suitability for different needs.
Pulse flow, also known as on-demand or intermittent flow (IF), delivers oxygen in short bursts or pulses when you inhale. It is designed to match your breathing pattern and conserve oxygen, making it more efficient for portable use and for individuals with lower oxygen requirements or active lifestyles. Pulse flow is generally used for portability exclusively because it conserves oxygen to extend battery life or activity time.
Continuous flow (CF), on the other hand, delivers a constant and steady flow of oxygen regardless of your breathing pattern. It is typically used for individuals with higher oxygen requirements or those who need a continuous supply of oxygen, such as during sleep or rest at home.
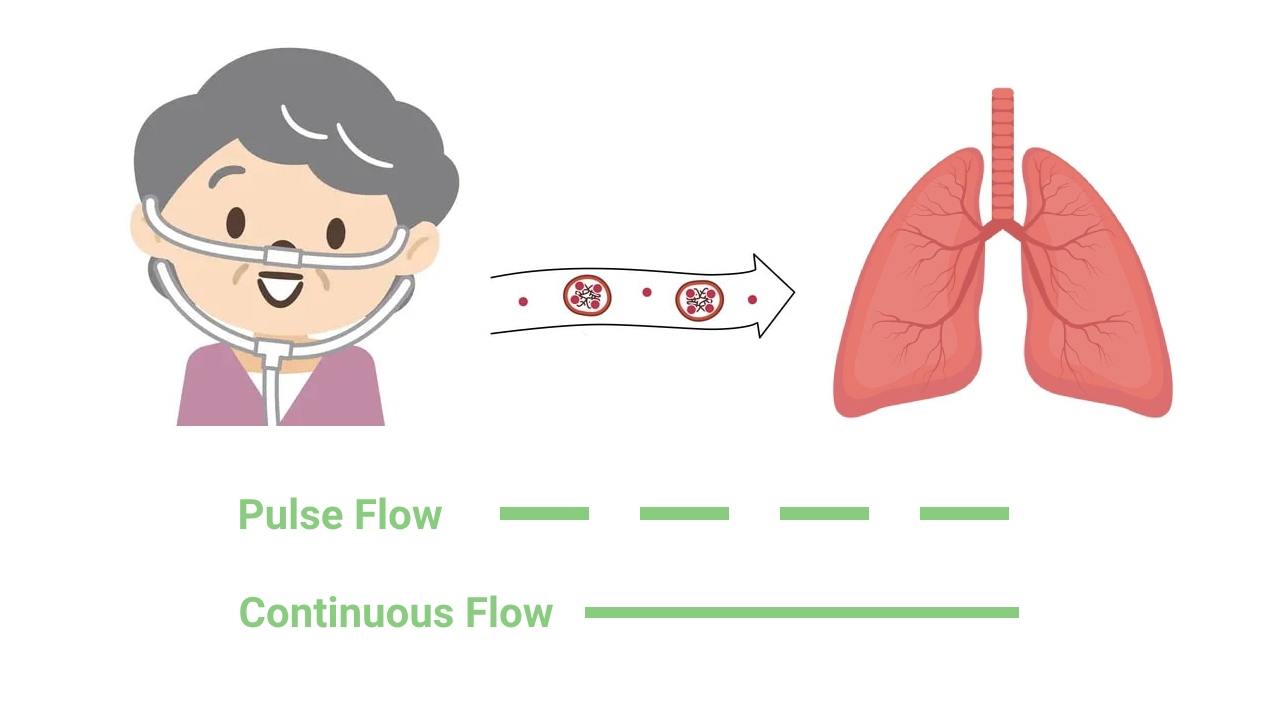
Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
Pulse Dose POC:
- Delivery:
- Flow Rate:
- Benefits:
- Lighter and more portable: Due to smaller size and lower battery consumption.
- Quieter operation: Less noisy compared to continuous flow models.
- More energy-efficient: Saves battery life, allowing for longer use on a single charge.
- Drawbacks:
- May not be suitable for all users: Individuals with severe respiratory conditions or specific oxygen delivery requirements might need continuous flow.
- Sensitivity to breathing patterns: Erratic or shallow breathing can affect oxygen delivery accuracy.
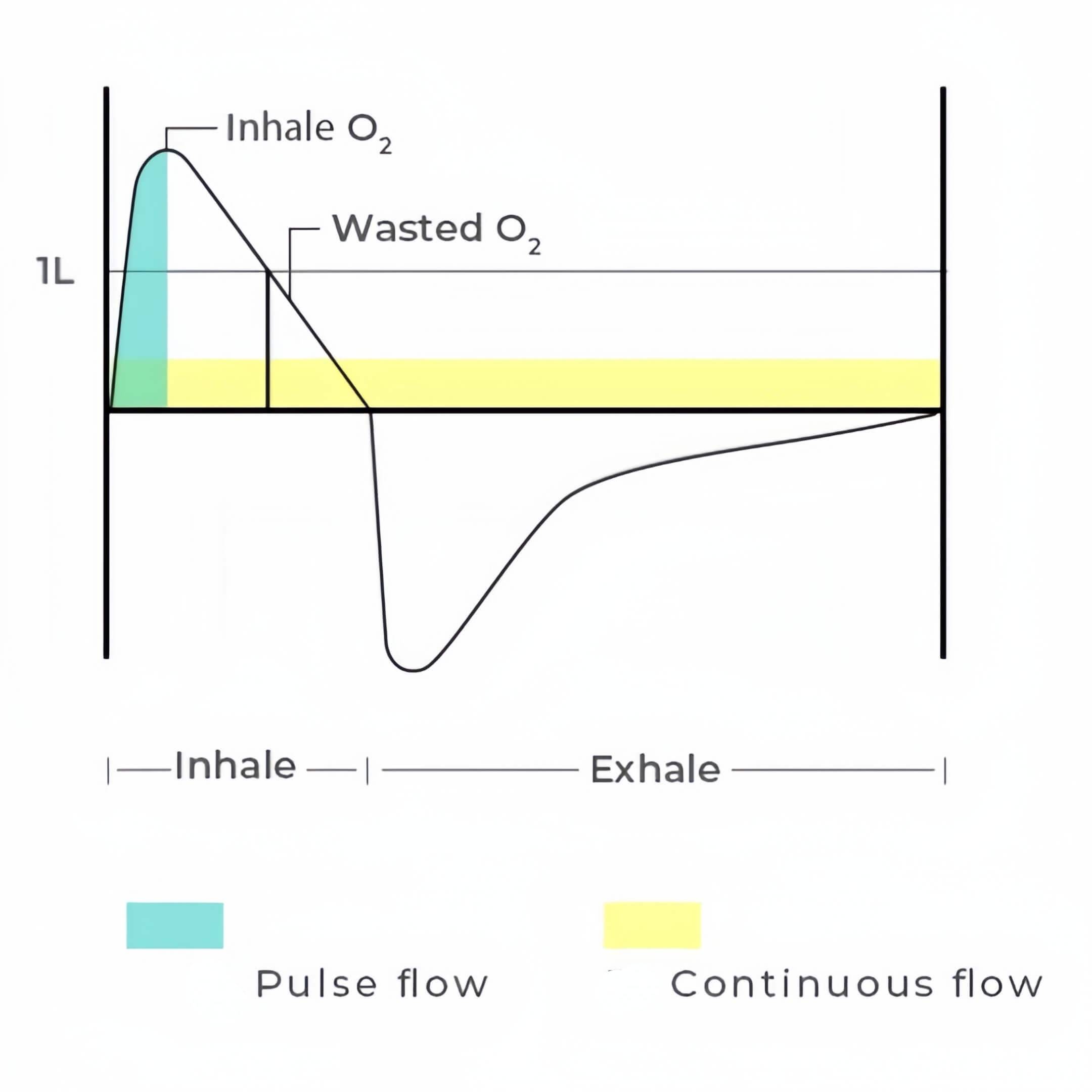
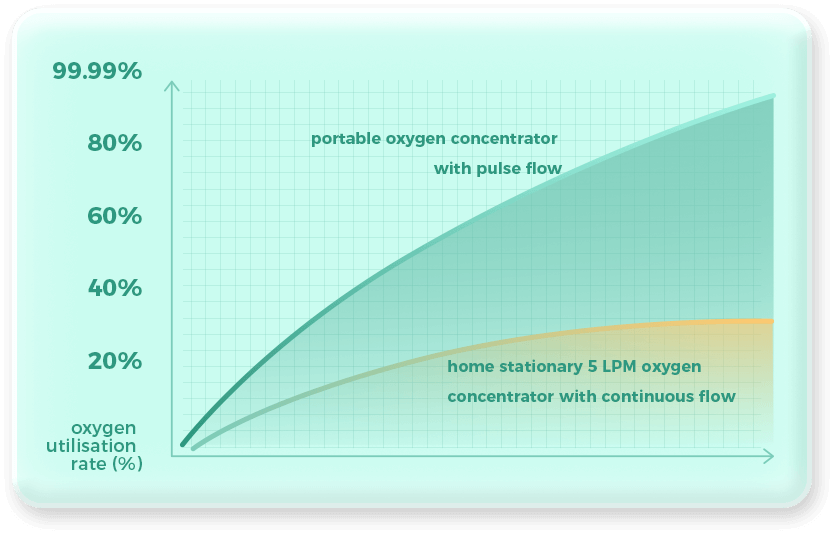
Continuous-flow POC:
- Delivery:
- Flow Rate:
- Benefits:
- Precise and consistent oxygen delivery: Suitable for users with critical oxygen needs or specific flow requirements.
- Unaffected by breathing patterns: Ensures consistent oxygen delivery even with shallow or irregular breathing.
- Drawbacks:
- Bulkier and heavier: Larger size and higher battery consumption limit portability.
- Louder operation: Can be noisier than pulse-flow models.
- Less energy-efficient: Requires more frequent battery charging.
Comparing Pulse Flow with Continuous Flow
- Chronic respiratory patients
- Breathless elderly individuals
- Sleep apnea sufferers
- End-of-life care patients
- Severe asthma/COPD patients
- While walking, hiking, driving in the car
- For plateau travel
- During social outings
- When attending events like concerts, sports games, etc.
- During mild to moderate exercise routines
- While sleeping
- While performing sedentary activities (reading, watching TV)
- During meals
- While doing seatting exercises
Choose the Right POC
The best type of POC for you depends on your individual needs and medical condition. Consulting your doctor is crucial to determine the most suitable option based on factors like:
- Severity of your respiratory condition
- Oxygen flow rate requirements
- Breathing patterns
- Activity level and lifestyle
- Portability needs
- Budget
By understanding the differences between pulse-flow and continuous-flow POCs and consulting your doctor, you can make an informed decision that optimizes your oxygen therapy and improves your quality of life.


