Atrial Flutter vs. AFib: What's the Difference?
What is Atrial Flutter?
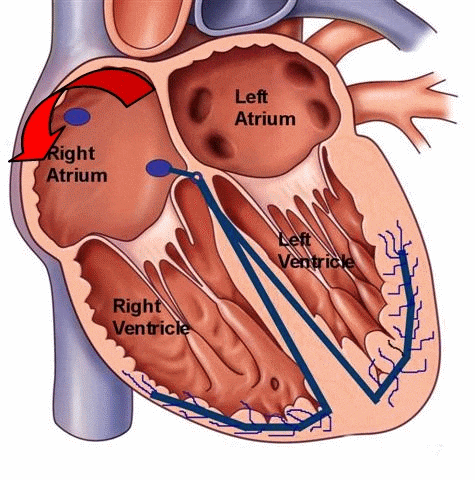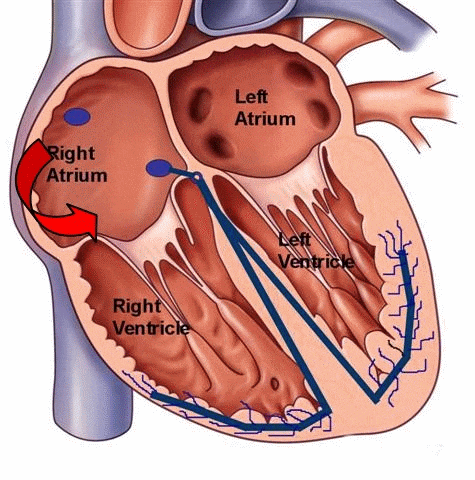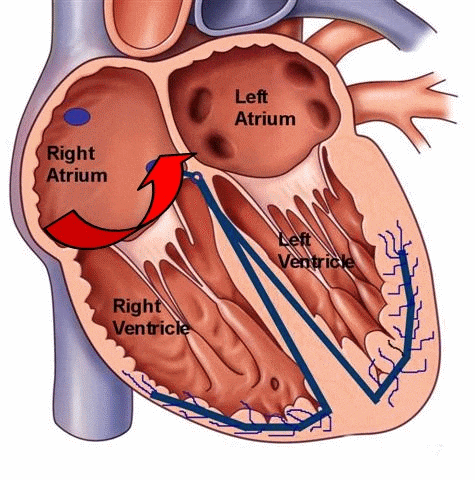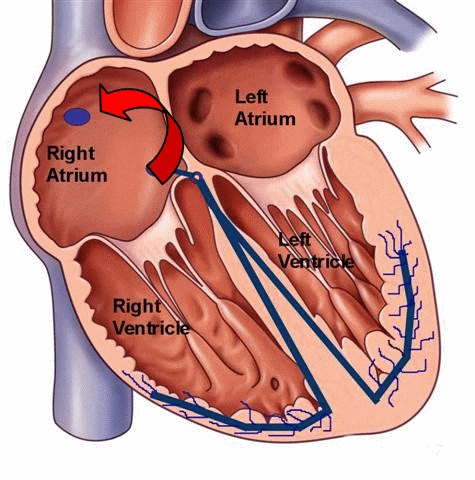
Atrial flutter refers to the abnormal electrical conduction pathway in the right atrium, which causes the atrium to beat too fast. The frequency of atrial ectopic pacemakers is 250 ~ 350 beats per minute. Atrial contraction is fast and coordinated, which is tachyarrhythmia between atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation. Common in organic heart disease such as rheumatic heart disease, coronary heart disease, hypertension heart disease, cardiomyopathy.
What Causes Atrial Flutter?
Atrial flutter mainly result from various heart diseases, such as rheumatic heart disease, coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, hypertensive heart disease, congenital heart disease and chronic congestive heart failure. Other causes include pulmonary embolism, hyperthyroidism, alcoholism and heart surgery.
Symptoms of Atrial Flutter
The patient's symptoms are mainly related to the duration of atrial flutter and ventricular rate.
Some people have no symptoms at all with atrial flutter. Others describe:
- Palpitations (rapid heartbeat or a pounding or fluttering sensation in the chest)
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety
- Trouble exercising
- Confusion
- Tiredness
In severe cases, may acute symptoms as below:
- Angina pectoris (chest or heart pains)
- Feeling faint or even cardiogenic shock
- Cough, hemoptysis, etc
What Is the Difference Between Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
Atrial flutter is closely related to AFib, both are atrial arrhythmias.
The differences include:
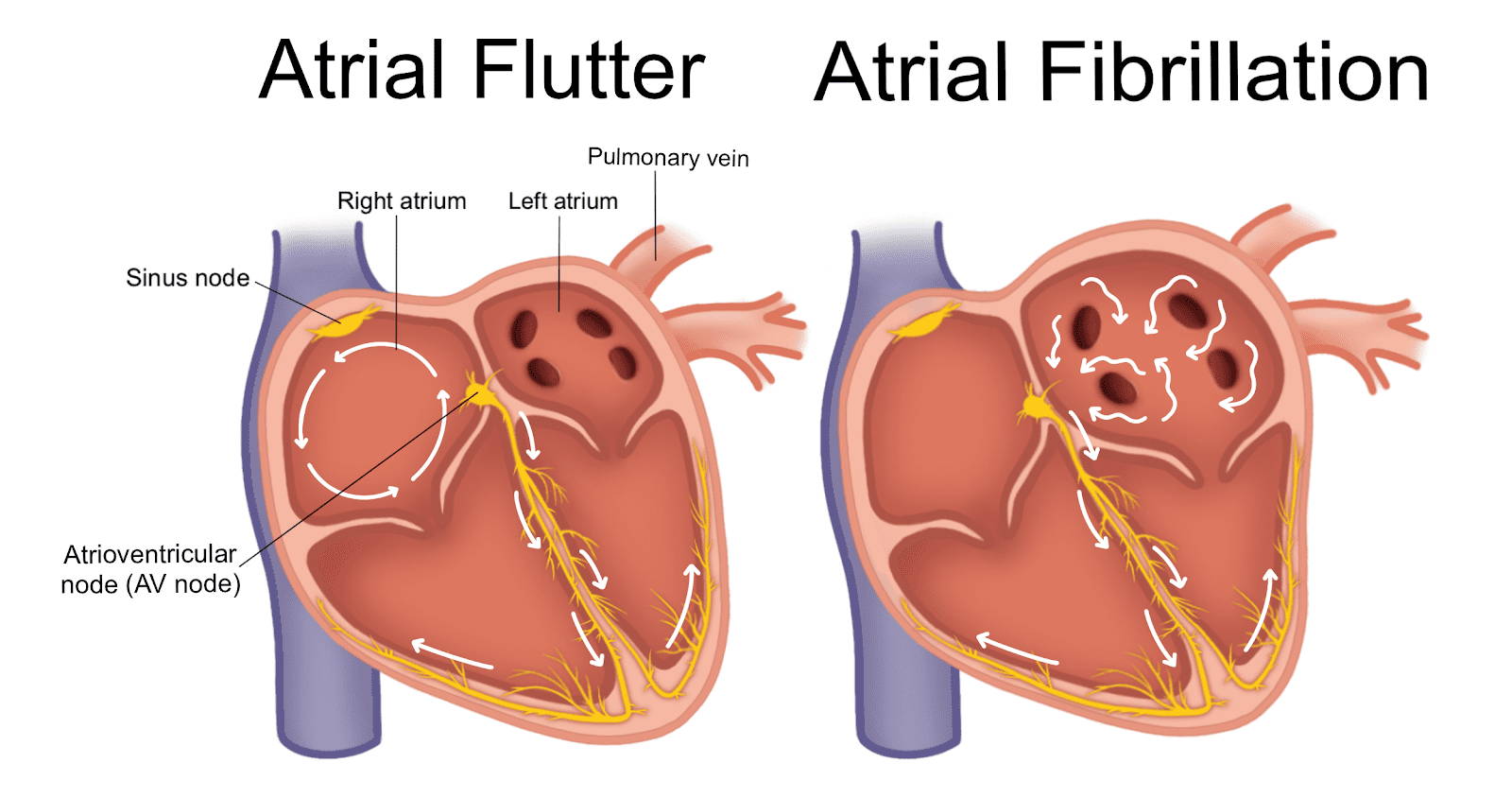
- Atrial flutter originates from the right atrium, and most atrial fibrillation is mainly caused by arrhythmias in the left atrium.
- Atrial flutter is an arrhythmia with regular atrial rhythm, electrical impulses move in a circle inside the upper chambers. This causes the heart to beat too fast but still in a steady rhythm. And atrial fibrillation is refers to the atrial electrical signals of absolute irregular disorder. This causes the heart to beat too fast and in a chaotic rhythm.
- The incidence of atrial fibrillation is higher than that of atrial flutter.
How to prevent Atrial Flutter?
Take active treatments of diseases that may cause atrial flutter, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, rheumatic heart valvular disease, hyperthyroidism, etc.
Keep light diets and take more fresh vegetables and fruits. Live in a regular life, prevent overwork and to exercise properly. Most importantly, keeping in good emotion.
How is an Atrial Flutter Diagnosed?
To diagnose an atrial flutter or find its cause, doctors usually use tests including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). The most common way to diagnose atrial flutter.
- Echocardiogram. This test uses ultrasound to check your heart muscle and valves, helps to determine whether there are structural abnormalities in the heart.
- Holter monitor (24-hour dynamic electrocardiogram). ECG/EKG monitoring time is too short to diagnose paroxysmal atrial flutter sometimes. Thus, a 24-hour dynamic electrocardiogram is commonly used in clinical to assist diagnosis. A Holter monitor not only can discover arrhythmias that are hard to discover at ordinary but also can statistics its occurrence frequency and clear severity.

Treatment for Atrial Flutter
Some patients can spontaneously restore sinus rhythm in a short time without treatment. If the patient is unable to recover on his own, individualized treatment plans should be developed, which can be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs, and electrical cardioversion or radiofrequency ablation if necessary.
author info

SIMEN D
Welcome to join in Wellue family. Let's share health information and find ways to keep in healthy from now on.


