What are the ECG Characteristics of Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia?
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is the most common type of sinus arrhythmia. It is more common in children, youth and the elderly, but less common in middle-aged people. The mechanism of respiratory sinus arrhythmia is that the tension of vagus nerve and sympathetic nerve changes during respiration, so that the self-discipline of sinoatrial node changes periodically and regularly.
The pressure receptors in the carotid sinus and aortic arch are stimulated when you inhale, causing the sympathetic nerve to excite, leading to an increased heart rate. When you exhale, it causes vagus tension to increase, resulting in a slow heart rate.
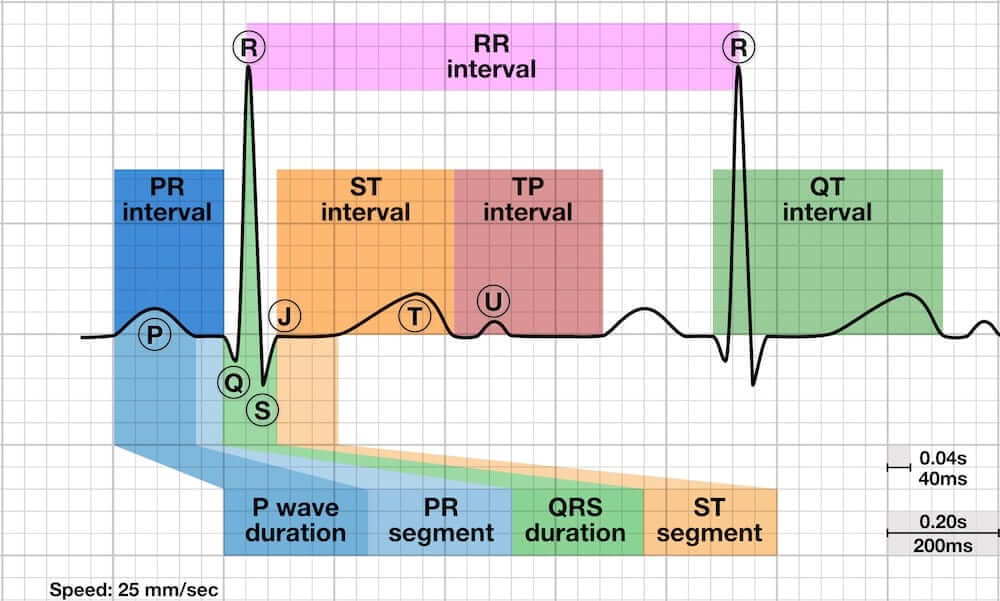
The cycle of heart rate change equaling to a respiratory cycle. The heart rhythm turns neat when you stop breathing. Its ECG/EKG characteristics are as follows:
- Variation in the P-P interval of more than 120 ms.
- The P-P interval gradually lengthens and shortens in a cyclical fashion, usually corresponding to the phases of the respiratory cycle.
- Normal sinus P waves with a constant morphology (no evidence of premature atrial contractions).
- Constant P-R interval (no evidence of Mobitz I AV block).
author info

SIMEN D
Welcome to join in Wellue family. Let's share health information and find ways to keep in healthy from now on.